EGB-Compact Electric Finger
Replacement for Pneumatic Fingers
Compact Size with High Output Force
Drop Detection
Replacement for Pneumatic Fingers
Compact Size with High Output Force
Drop Detection

| Item | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
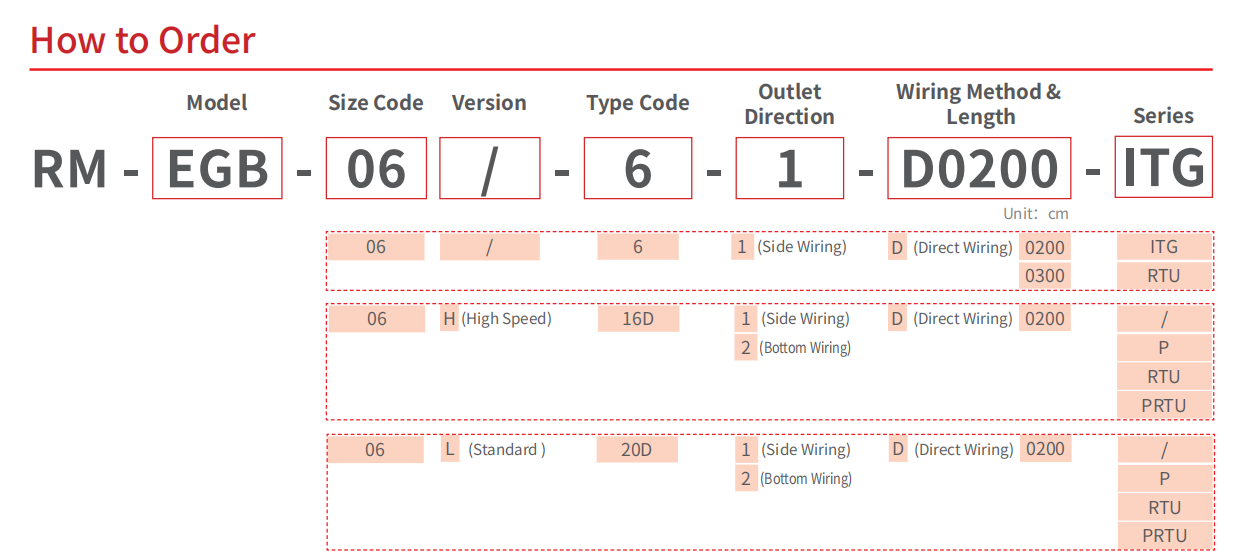
| Model | Model | RM-EGB-06-6-ITG | RM-EGB-06H-16D | RM-EGB-06L-20D |
| Size Code | 06 | 06H | 06L | |
| Weight (kg) | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.32 | |
| Dimensions (mm) | 98*38*23.5 | 98*38*23.5 | 108*50*27.6 | |
| Performance | Stroke (mm) | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| Gripping Force1 (N) | 10/20/30/40 (Four levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
10/15/35/60 (Four levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
16/30/60/80 (Four levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
|
| Absolute Position (mm) | 0/2/4 (Three levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
0/2/4 (Three levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
0/4/8 (Three levels are optional, and I/O combination triggering requires no parameter adjustment.) |
|
| Repeat Positioning Accuracy (mm) | ±0.02 | ±0.02 | ±0.02 | |
| Max. Opening/Closing Time (s) | 0.3/0.3 | 0.1/0.1 | 0.18/0.18 | |
| Permissible Load Torque (N.m) | MR: 1.36, MP: 0.8, MY: 0.68 | MR: 1.36, MP: 0.8, MY: 0.68 | MR: 2.65, MP: 2.35, MY: 1.65 | |
| Control Mode | Controller | Controller Built-in | Controller Built-in | Controller Built-in |
| "-ITG" Series or "-/" Series | I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points | I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points | I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points | |
| "-P" Series | / | / | / | |
| "-RTU" Series | I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points Modbus RTU |
I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points Modbus RTU |
I/O (NPN) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points Modbus RTU |
|
| "-PRTU" Series | / | I/O (PNP) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points Modbus RTU | I/O (PNP) Input 3 Points, Output 3 Points Modbus RTU | |
| Operating Environment | Rated Voltage (V) | DC24±10% | DC24±10% | DC24±10% |
| Rated Current (A) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |
| Peak Current (A) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | |
| Usage Environment | 0~40°C, <85%RH (Without condensation) | |||
| Protection Class IP | IP40 | IP40 | IP40 | |
RM-EGB compact electric finger is a highly integrated unit with a built-in controller, featuring four preset force levels and three preset stroke levels. Installation and commissioning are simple and require no parameter settings, making it ideal for directly replacing pneumatic grippers of the same compact size.
The EGB supports two control methods: I/O and Modbus RTU.
If other communication methods are required, please refer to RobustMotion's other intelligent electric actuator series.
Taking RM-EGB-06 as an example, its maximum force is 40 N.
RM-EGB is available in different motion speed specifications. RM-EGB-06H-16D is the high-speed version. Its maximum opening and closing speed is 0.1 s for opening and 0.1 s for closing, which is theoretically faster than pneumatic grippers of the same specification.
The allowable load of the gripper depends on the length of the tooling or fixtures and the weight of the load. Please refer to the product catalog for detailed specifications.
Servo motor.
No. It does not include a mechanical self-locking (brake) mechanism.
Yes. RM-EGB delivers high force output in a compact size, making it suitable for applications with space limitations.
RM-EGB Comapct Electric Finger not only serves as a direct replacement for pneumatic grippers but also incorporates a drop-detection function that conventional pneumatic grippers do not have. It provides immediate signal feedback whenever a workpiece is not gripped or is dropped.
RM-EGB Comapct Electric Finger is used in a wide range of automation applications across industries such as 3C, optics, and medical aesthetics. It is ideal for tasks like synchronized gripping and transferring of electronic components in compact spaces during processes such as loading and unloading.